Troubleshooting Dehydration Feed Separator
Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD) simulations were applied in detailed analysis of flow distribution and performance for a Dehydration FEED Separator. Modelling revealed slugging in the upstream piping. Simulations also addressed gas flow patterns inside the vessel to verify the adequacy of separation performance and explore scope for upgrade.

Business Problem
An LNG facility, located in Asia, reported operational issues in Dehydration Feed Separators. A pair of separators, each handling 450 MMSCFD of gas, were designed to capture liquids upstream of dehydration units. Degraded performance of the dehydration units over time was attributed to liquid carry-over from the separators. The customer commissioned a detailed independent study to determine the cause of excessive carry-over and to identify remedies. Degradation of dehydration resulted in excessive down time with lost production and costly replacement of molecular sieve bed material.
Analysis
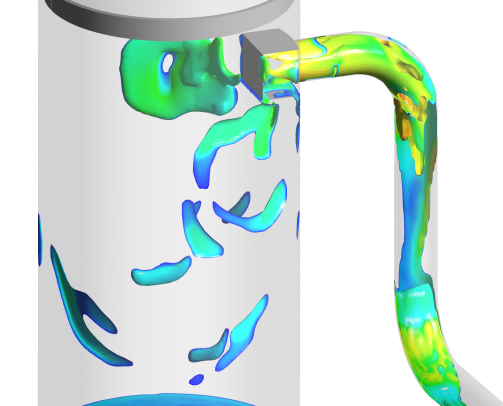
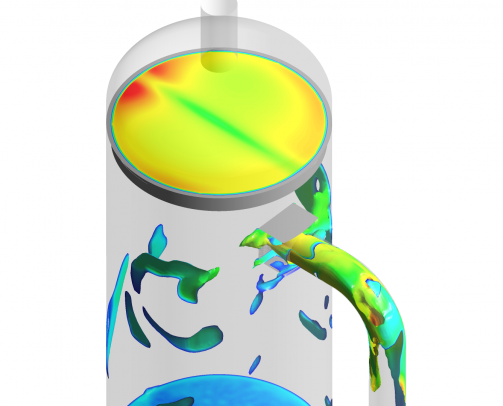
Computational fluid dynamics indicated substantial slugging of the fluids entering the Dehydration Feed Separator, caused by process flow conditions and the configuration of upstream piping. In addition to this, the vessel featured a deflector plate inlet device.
CFD Simulations and associated analysis provided the following:
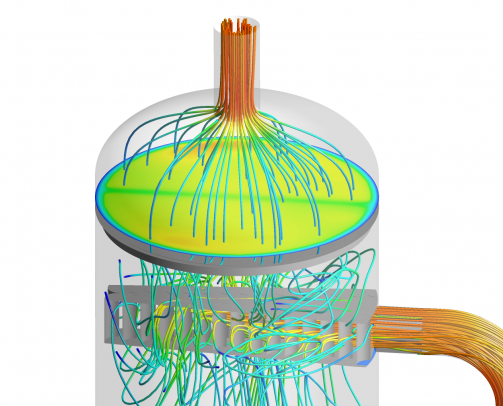
- Visualisation of gas flow distribution throughout the vessel
- Flow distribution and slugging of liquid
- Droplet shear & re-entrainment evaluation
- Droplet tracking of liquid (DPM), with liquid load evaluation and separation efficiency evaluation for demisting
- Overall separation performance evaluation
The inlet deflector causes severe droplet shearing, adding to the mist loading. This is coupled with pronounced maldistribution of the vapour flow throughout the separator, which in turn promotes local overloading of demisting equipment. Modelling demonstrated the impact of the combination of issues and with additional analysis in MySep software, quantified the magnitude of carry-over.

Solution
As well as slug flow it was found that the configuration of the inlet piping promoted swirl to the flow entering the separator. Kranji specified a swirl elimination device upstream of the inlet nozzle. Droplet shearing and gas flow maldistribution within the vessel were minimised by adoption of a vane-type inlet device. CFD analysis of the retrofit solutions demonstrated improved operational stability and satisfactory separation performance over the operating range.
Summary
Expert application of CFD modelling diagnosed the factors contributing to poor separation performance in a pair of Dehydration Feed Separators. Retro-fit solutions were specified, and their effectiveness confirmed by further CFD simulation and subsequently by client feedback after the implementation.
Benefit Analysis:
- Visualization and quantification of poor design practice
- Identification of cost-effective retrofit remedial measures
- Increased molecular sieve bed life
- Increased production run times with plant “bottom line” impact

Interested?
Are you looking for troubleshooting, root cause analysis, debottlenecking or capacity increase of your equipment?
